Our customer service representatives are available 24 hours a day, from Monday to Sunday.
| Catalog Number | CI-HC-0011 |
| Product Name | SM Cocoyl Taurate |
| CAS | 61791-42-2 |
| Description | Mild anionic solid surfactant derived from coconuts. 25% active detergent. |
| Solubility | Water-soluble |
| Appearance | Soft, off-white paste |
| Application | Shampoos, detergent bars, bubble bath, shower gels but also facial cleansers due to its mildness. |
| Storage | Store in a closed container at a dry place at room temperature |
| Composition | Sodium methyl cocoyl taurate |
| Features And Benefits | Good degreasing but still very mild cleansing agentHas very good foam boosting and lathering propertiesIdeal replacement for SLD (sodium lauryl sulfate)Hard water tolerant and stable over wide pH range. The foaming and lathering properties in hard or soft matter resemble those of soap in soft water. |
| GMO | GMO-free |
| HS Code | 3402319000 |
| INCI | Sodium methyl cocoyl taurate |
| Manufacture | Sodium methyl cocoyl taurate is produced by reacting N-methyltaurine with coconut fatty acids followed by neutralization with sodium hydroxide. |
| Preservation | Preservative-free |
| Purity Grade | No purity grade applicable |
| Raw Material Source | Monochloroacetic acid |
| Uses | Can be added to formulas as is, recommended use level 1 - 50%. Can be used as co-surfactant with other surfactants (anionic or nonionic). For external use only. |
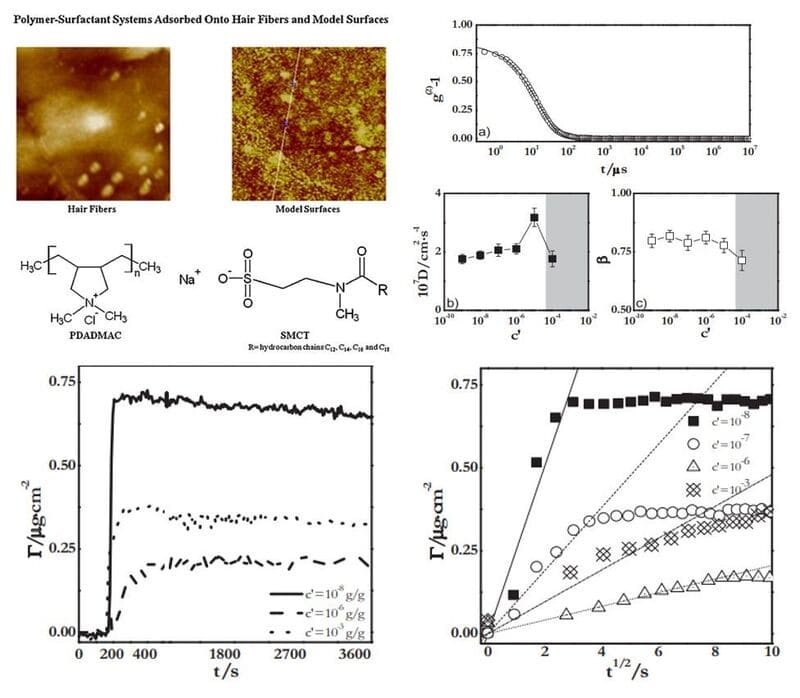 Llamas, Sara, et al. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2016, 505, 150-157.
Llamas, Sara, et al. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2016, 505, 150-157.
Sodium methyl cocoyl taurate (SMCT) is a sulfate-free surfactant commonly used in shampoo and hair care formulations. In this work, the adsorption of supramolecular complexes formed by highly charged cationic homopolymers (polydiallyldimethylammonium chloride, PDADMAC) and sulfate-free anionic surfactant SMCT on liquid/solid interfaces was studied. Understanding the physicochemical mechanism of PDADMAC-SMCT complexes is useful for the design of cosmetic conditioner formulations.
Key Findings
· Throughout the entire range of surfactant concentrations studied, which extends beyond the critical micelle concentration (cmc) and into the precipitation area, the ζ-potential did not exhibit charge inversion.
· Dynamic light scattering measurements revealed a significant increase in aggregate size as the phase region initiated, corroborated by heightened turbidity in the solutions and dispersions. The adsorption onto negatively charged solid substrates is closely linked to the charge of the bulk complexes, with the kinetics of layer adsorption being diffusion-controlled.
· This research indicates that PDADMAC-SMCT mixtures adsorb effectively onto negatively charged surfaces, with characteristic adsorption times comparable to the time conventional shampoos are typically applied to hair. Thus, PDADMAC-SMCT mixtures present a promising option for formulating sulfate-free shampoos and conditioners.
 Virk, Akashdeep Singh, et al. Available at SSRN 5073745.
Virk, Akashdeep Singh, et al. Available at SSRN 5073745.
This case presents the formulation methodology of a cleansing shampoo product which includes sodium methyl cocoyl taurate as a key ingredient.
This shampoo formulation aims to eliminate hair oil and impurities through the use of sodium methyl cocoyl taurate. It is also effective for scalp-cleansing formulations. Good lathering and smooth texture result from combining sodium methyl cocoyl taurate with sodium C14-16 olefin sulfonate. AMP and basic amino acids help clean away dirt while amino acids improve the experience for the user.
Formulation Steps
1) Disperse Polyquaternium-10 (high viscosity, low amine) in purified water by heating to 80°C, then incorporate EDTA-2Na and sodium benzoate. (B)
2) Mix PEG-20 sorbitan cocoate with the fragrance before homogenizing the solution. (C)
3) Mixtures B should receive sodium methyl cocoyl taurate and sodium C14-16 olefin sulfonate together with cocamide propyl betaine along with cocamide methyl MEA. (A + B)
4) After cooling the mixture to 45°C, combine it with C and then add methyl isothiazolinone along with AMP, arginine, and glutamic acid. (B + A + C + D)
5) Regulate the pH level using 50% citric acid and incorporate water if necessary.